Settings & Buttons¶
Adding Files¶
EDA Playground supports multiple files, up to a total character limit of 1,000,000. The files may be HDL source files, or text files to be used as inputs to the testbench.
To add a file, click the + sign in the testbench or design pane. Then create a new file or upload an existing file. The filename may not contain special characters.
Simulating code with multiple files
For SystemVerilog, use include statements such as the following to include the added source files in the compile:
`include "adpcm_seq_item.svh"
For VHDL, all files with the .vhd and .vhdl extensions are automatically included in the compile.
For Python, use import statements:
from design import *
To rename a file, double click the tab name. (The initial testbench and design files cannot be renamed.)
Sidebar Options¶
EDA Playground provides many options that can be configured for running your code.
Languages & Libraries¶
This section allows selection of coding languages and the available libraries for those languages.
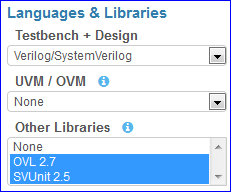
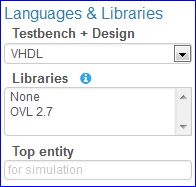
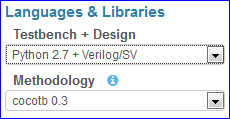
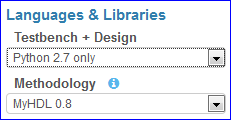
Testbench + Design¶
The testbench (left editor pane) and design (right editor pane) may be written using one of these languages:
Verilog/SystemVerilog for both
VHDL for both
e for testbench, and SystemVerilog/Verilog for design
Python for testbench, and SystemVerilog/Verilog for design
Python for both
UVM / OVM (SystemVerilog)¶
When language is Verilog/SystemVerilog, a UVM or OVM library can be used for both the design and testbench. The following libraries are available:
UVM 1.2
UVM 1.1d
OVM 2.1.2
Other Libraries (SystemVerilog/Verilog)¶
When language is Verilog/SystemVerilog, other Verilog libraries can be used for both the design and testbench. These libraries may be used along with UVM/OVM. Multiple libraries may be selected at the same time. Ctrl+Click to select multiple libraries. Available libraries:
OVL
SVUnit
ClueLib
svlib
SVAUnit
Libraries (VHDL)¶
When language is VHDL, the following VHDL libraries can be used for both design and testbench.
OVL
OSVVM
UVVM
Top entity (VHDL)¶
When language is VHDL, the top entity of the design must be specified before running a simulation.
Libraries (C++)¶
When language is C++/SystemC, the following libraries can be used for both design and testbench.
SystemC 2.3.1
SystemC 2.3.0
Methodology (Python + Verilog or Python only)¶
When testbench language is Python and design language is Verilog/SystemVerilog, the following verification environments are available:
cocotb 0.4
cocotb 0.3
cocotb 0.2
When testbench and design language is Python, the following methodologies are available:
MyHDL 0.8
Migen X
Migen¶
Before running synthesis on a Migen design, the Top class corresponding to the top module must be specified. The Top class is the class instantiation to use when converting the Migen design to Verilog. Some examples:
MyModule()Divisor(4)MyMemory(16, 2**12, init=list(range(20)))
Tools & Simulators¶
For running the code, several tools/simulators may be selected. Many simulators have additional options that may be specified. Any options needed for languages and libraries will automatically be included.
Open EPWave after run¶
Checking this option will open EPWave wave viewer in a new window after the simulation run completes (pop-ups must be enabled). It is available for all simulators that have a run step.
Download files after run¶
Checking this option will download the run directory as a ZIP file after the simulation run (pop-ups must be enabled). The simulation run does not have to be successful for the download to occur. The ZIP file will include all the code files as well as any generated files such as wave dumps, log files, etc.
YouTube video: How to download code and results from EDA Playground
Simulators¶
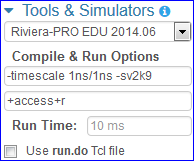
Additional command-line compile options and run options may be specified in the bottom textboxes.
(If available), the Run Time option can be used to specify the number of timesteps for the simulation to run. By default, the simulation runs forever until it hits a breakpoint or $finish.
The Use run.do Tcl file option is for using a custom run.do DO file for specifying simulation commands. To use a run.do Tcl file, check the option and add a new file called ‘run.do’.
Yosys¶
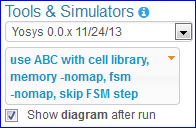
Yosis is a synthesis tool for performing logical synthesis and creating a netlist. It supports using ABC to synthesize for a sample cell library.
Yosys will only process code in the right Design pane. The code in the left Testbench pane will be ignored. UVM/OVM/Methodology/Libraries selections are also ignored.
The following synthesis options are available:
use ABC with cell library - synthesize for a demo cell library using ABC
memory -nomap - skip memory_map step
fsm -nomap - skip fsm_map step
skip FSM step
Show diagram after run - open the generated circuit diagram after synthesis flow completes (pop-ups must be enabled).
When using Yosys with Migen, the Top class must be specified, which is used to convert Migen design to Verilog.
When using Yosys with MyHDL, the Testbench pane must contain code to convert MyHDL design to a Verilog file. The Verilog file must have suffix .v, and can be named anything EXCEPT tb_* or a Verilog reserved keyword. Thus, when running Yosys on MyHDL code, the Testbench code will be run first before synthesis.
VTR¶
Verilog-to-Routing is a complete physical design flow that includes elaboration, logical sysnthesis, FPGA technology mapping, packing, placement, and routing. The recommended architecture file k6_frac_N10_mem32K_40nm.xml is used for the flow. In addition, route channel width is set at a high 100 to ensure no routing issues with dense designs.
VTR will only process code in the right Design pane. The code in the left Testbench pane will be ignored. UVM/OVM/Methodology/Libraries selections are also ignored. Currently, no additional options are available for VTR.
Currently, VTR cannot be used with MyHDL or Migen.
Share Tab¶
You can add a name and description for your playground using the share tab (which can be found in the bottom pane).
A brief name/title of the playground. Visible by others when they open a saved playground.
A longer description of the playground. Visible by others when they open a saved playground. You can format your text using Markdown.
You can control the visibility of your playground by selecting one of three options:
Private (only your can view)
Public (anyone with the link can view)
Published (will appear in search results)
Examples¶
Links to code examples created on EDA Playground. These generate a search of the EDA Playground database.
Editor Modes and Shortcuts¶
The editor supports the following modes:
Default
Vim
Emacs
The user may select the mode in the User Options on the user page:
Note that Vim and Emacs modes are only loose approximations of the actual bindings.
Default Mode¶
The default mode comes with search/replace functionality. The keybindings are:
Ctrl-F / Cmd-F - Start searching
Ctrl-G / Cmd-G - Find next
Shift-Ctrl-G / Shift-Cmd-G - Find previous
Shift-Ctrl-F / Cmd-Option-F - Replace
Shift-Ctrl-R / Shift-Cmd-Option-F - Replace all
The default mode uses the following shortcuts. Note that the shortcuts are different for PC and MAC users.
// For All
keyMap.basic = {
"Left": "goCharLeft", "Right": "goCharRight", "Up": "goLineUp", "Down": "goLineDown",
"End": "goLineEnd", "Home": "goLineStartSmart", "PageUp": "goPageUp", "PageDown": "goPageDown",
"Delete": "delCharAfter", "Backspace": "delCharBefore", "Tab": "defaultTab", "Shift-Tab": "indentAuto",
"Enter": "newlineAndIndent", "Insert": "toggleOverwrite"
};
// For PC
keyMap.pcDefault = {
"Ctrl-A": "selectAll", "Ctrl-D": "deleteLine", "Ctrl-Z": "undo", "Shift-Ctrl-Z": "redo", "Ctrl-Y": "redo",
"Ctrl-Home": "goDocStart", "Alt-Up": "goDocStart", "Ctrl-End": "goDocEnd", "Ctrl-Down": "goDocEnd",
"Ctrl-Left": "goGroupLeft", "Ctrl-Right": "goGroupRight", "Alt-Left": "goLineStart", "Alt-Right": "goLineEnd",
"Ctrl-Backspace": "delGroupBefore", "Ctrl-Delete": "delGroupAfter", "Ctrl-F": "find",
"Ctrl-G": "findNext", "Shift-Ctrl-G": "findPrev",
"Ctrl-[": "indentLess", "Ctrl-]": "indentMore",
fallthrough: "basic"
};
// For MAC
keyMap.macDefault = {
"Cmd-A": "selectAll", "Cmd-D": "deleteLine", "Cmd-Z": "undo", "Shift-Cmd-Z": "redo", "Cmd-Y": "redo",
"Cmd-Up": "goDocStart", "Cmd-End": "goDocEnd", "Cmd-Down": "goDocEnd", "Alt-Left": "goGroupLeft",
"Alt-Right": "goGroupRight", "Cmd-Left": "goLineStart", "Cmd-Right": "goLineEnd", "Alt-Backspace": "delGroupBefore",
"Ctrl-Alt-Backspace": "delGroupAfter", "Alt-Delete": "delGroupAfter", "Cmd-F": "find",
"Cmd-G": "findNext", "Shift-Cmd-G": "findPrev",
"Cmd-[": "indentLess", "Cmd-]": "indentMore",
fallthrough: ["basic", "emacsy"]
};
keyMap.emacsy = {
"Ctrl-F": "goCharRight", "Ctrl-B": "goCharLeft", "Ctrl-P": "goLineUp", "Ctrl-N": "goLineDown",
"Alt-F": "goWordRight", "Alt-B": "goWordLeft", "Ctrl-A": "goLineStart", "Ctrl-E": "goLineEnd",
"Ctrl-V": "goPageDown", "Shift-Ctrl-V": "goPageUp", "Ctrl-D": "delCharAfter", "Ctrl-H": "delCharBefore",
"Alt-D": "delWordAfter", "Alt-Backspace": "delWordBefore", "Ctrl-K": "killLine", "Ctrl-T": "transposeChars"
};
Buttons¶
EDA Playground Logo¶
Click on the EDA Playground logo to launch a new playground.
Run¶
Shortcut: Ctrl+Enter
Run the current code using the selected tool/simulator and options. The code runs on the EDA Playground server and the results are printed in the bottom Results pane.
Save¶
Shortcut: Ctrl+S
Save the current playground, including code, bottom 200 lines of results, and options. Once the playground is saved, the page reloads. The location specified in the address bar is a static link to this playground – this link can be shared with others.
If the playground has been saved previously, clicking on Save updates the currently saved playground. The static link does not change.
If you modified a code example but did not save, you’ll see an asterisk in the Save button.
Copy¶
This button shows up for everyone when viewing a saved playground. Clicking on it creates a new copy of the current playground. The copy will be complitely separate from the original, and it will have its own link that can be shared with others.
If you modified a code example but did not save, you’ll see an asterisk in the Copy button.
?¶
Links to EDA Playground documentation (these pages).
Flask¶
Shows links to other apps available on EDA Playground, such as EPWave.
Playgrounds¶
Gives access to your and others’ playgrounds. You can either browse or search.
Log In / Profile¶
The user must be logged in to save or run playground code. Playground code and results may be viewed without logging in. If this button says “Log in” then click it to log in.
If this button says “Profile”, then you can click it to access your profile and your settings or to log out.
Log In¶
The user must be logged in to save or run playground code. Playground code and results may be viewed without logging in.
Collaborate¶
Allows real-time collaborations where multiple users can edit code simultaneously.
Real-Time Collaboration Intro on YouTube.
Forum¶
A short cut to the EDA Playground Forum.
Follow @edaplayground¶
Click to follow EDA Playground on Twitter.

